


Compass

Description of Compass
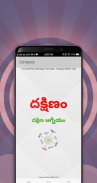
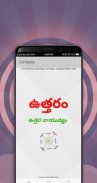
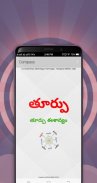
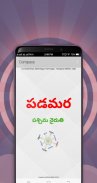
A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions (or points). Usually, a diagram called a compass rose shows the directions north, south, east, and west on the compass face as abbreviated initials. When the compass is used, the rose can be aligned with the corresponding geographic directions; for example, the "N" mark on the rose points northward. Compasses often display markings for angles in degrees in addition to (or sometimes instead of) the rose. North corresponds to 0°, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90° degrees, south is 180°, and west is 270°. These numbers allow the compass to show magnetic North azimuths or true North azimuths or bearings, which are commonly stated in this notation. If magnetic declination between the magnetic North and true North at latitude angle and longitude angle is known, then direction of magnetic North also gives direction of true North.
Among the Four Great Inventions, the magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han Dynasty (since c. 206 BC, and later adopted for navigation by the Song Dynasty Chinese during the 11th century. The first usage of a compass recorded in Western Europe and the Islamic world occurred around 1190
Modern compasses usually use a magnetized needle or dial inside a capsule completely filled with a liquid (lamp oil, mineral oil, white spirits, purified kerosene, or ethyl alcohol are common). While older designs commonly incorporated a flexible rubber diaphragm or airspace inside the capsule to allow for volume changes caused by temperature or altitude, some modern liquid compasses utilize smaller housings andor flexible capsule materials to accomplish the same result. The liquid inside the capsule serves to damp the movement of the needle, reducing oscillation time and increasing stability. Key points on the compass, including the north end of the needle are often marked with phosphorescent, photo luminescent, or self-luminous materials to enable the compass to be read at night or in poor light. As the compass fill liquid is non compressible under pressure, many ordinary liquid-filled compasses will operate accurately underwater to considerable depths.


























